-
-
-
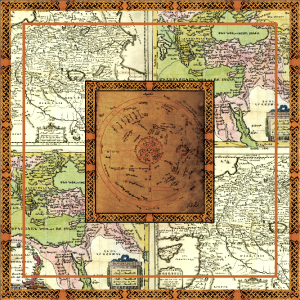
“Armenian Maps” Scarf
The oldest extant map of the world is depicted on a clay tablet. It is the Babylonian map found in Iraq, in 19 century. Now it is stored in the British Museum.
This Babylonian map of the World dates back to 6 century BC. In ancient Assyrian and Babylonian sources the kingdom of Ararat is referred to as Urartu. This name is mentioned on the world’s oldest map. Of the countries mentioned in this map, only Armenia still exists. All the other ones have disappeared from the world map.
https://www.armgeo.am/en/armenia-on-the-oldest-maps-of-the-world/$50.00 – $110.00 -
“Armenian Alphabet” Scarf
The Armenian alphabet was created in 405 AD.
One of the greatest marks of the Armenian identity is the Armenian language. The exact origins of the Armenian language, however, are a little bit obscure. Such is the case with many ancient languages. Serious scholarship starting from the 19th century has placed Armenian among the wider family of Indo-European languages, although it forms its own separate branch within that group. So the language does not have any close relatives today, even Indo-European ones, such as Spanish and Portuguese or Russian and Polish might be considered.Armenian is also unique in its writing system. The Armenians use their own alphabet which was, by tradition, created following the studies and meditations of a monk, Mesrop Mashtots, in the early 5th century AD. Christianity had already been accepted as the national religion for a hundred years in Armenia, but the Bible was not yet available in the native language. The tradition goes that the main motivation to come up with a separate Armenian alphabet was in order to translate the Bible in such a way that would be accessible and suitable for the language and the people.
Mesrop Mashtots – who has since been venerated as a saint, as the patron of teaching and learning for Armenians – accomplished the task in the year 405 AD, thus setting the stage for a rich trove of works of religion and history, science and philosophy, illuminated manuscripts, and published books in the millennium and a half that followed, continuing on today. A major road in the capital of Armenia, Yerevan, is named for Mashtots, and one end of it is the apt location for the Matenadaran, the national repository of manuscripts which also functions as a research institute and museum.
$110.00 -
“Yerevan Love” Scarf
Inspired by the city of Yerevan and the love each and every Armenian feels for the city.
The history of Yerevan dates back to the 8th century BCE, with the founding of the fortress of Erebuni in 782 BCE by King Argishti I at the western extreme of the Ararat plain. Erebuni was “designed as a great administrative and religious centre, a fully royal capital.” By the late ancient Armenian Kingdom, new capital cities were established and Yerevan declined in importance. Under Iranian and Russian rule, it was the center of the Erivan Khanate from 1736 to 1828 and the Erivan Governorate from 1850 to 1917, respectively. After World War I, Yerevan became the capital of the First Republic of Armenia as thousands of survivors of the Armenian genocide in the Ottoman Empire arrived in the area. The city expanded rapidly during the 20th century as Armenia became part of the Soviet Union. In a few decades, Yerevan was transformed from a provincial town within the Russian Empire to Armenia’s principal cultural, artistic, and industrial center, as well as becoming the seat of national government.
With the growth of the Armenian economy, Yerevan has undergone major transformation. Much construction has been done throughout the city since the early 2000s, and retail outlets such as restaurants, shops, and street cafés, which were rare during Soviet times, have multiplied. As of 2011, the population of Yerevan was 1,060,138, just over 35% of Armenia’s total population. According to the official estimate of 2016, the current population of the city is 1,073,700. Yerevan was named the 2012 World Book Capital by UNESCO.[28] Yerevan is an associate member of Eurocities.$110.00 -
“Cuneiform” Silk Scarf
In the mid-9th century BC, one of the most powerful states of the Ancient Near East, known as Urartu from Assyrian inscriptions, came down to the historic scene in the Armenian Highland. The Urartians called their country Biainili. It is mentioned as the Araratian Kingdom in the Bible.
Artefacts found, bear witness to a highly developed civilization of ancient Eastern type with a solid state system, literature, original ritual-religious system, prospering towns, crafts and arts. Urartu collapsed in the struggle against the Medians, Babylonians and Scythians in 585 BC. After the decline of the Urartian statehood, the kingdom of the Armenian Yervandids (Orontids) was formed on the same territory.
$90.00 -
“Trchnagir” Alphabet
The Armenian alphabet was created in 405 AD.
One of the greatest marks of the Armenian identity is the Armenian language. The exact origins of the Armenian language, however, are a little bit obscure. Such is the case with many ancient languages. Serious scholarship starting from the 19th century has placed Armenian among the wider family of Indo-European languages, although it forms its own separate branch within that group. So the language does not have any close relatives today, even Indo-European ones, such as Spanish and Portuguese or Russian and Polish might be considered.Armenian is also unique in its writing system. The Armenians use their own alphabet which was, by tradition, created following the studies and meditations of a monk, Mesrop Mashtots, in the early 5th century AD. Christianity had already been accepted as the national religion for a hundred years in Armenia, but the Bible was not yet available in the native language. The tradition goes that the main motivation to come up with a separate Armenian alphabet was in order to translate the Bible in such a way that would be accessible and suitable for the language and the people.
Mesrop Mashtots – who has since been venerated as a saint, as the patron of teaching and learning for Armenians – accomplished the task in the year 405 AD, thus setting the stage for a rich trove of works of religion and history, science and philosophy, illuminated manuscripts, and published books in the millennium and a half that followed, continuing on today. A major road in the capital of Armenia, Yerevan, is named for Mashtots, and one end of it is the apt location for the Matenadaran, the national repository of manuscripts which also functions as a research institute and museum.
$110.00“Trchnagir” Alphabet
$110.00 -
Spring Ornamental
Inspired by the traditional Armenian ornaments and motifs.
$110.00Spring Ornamental
$110.00 -
“Abstract Rose” Silk Scarf
Available 2 sizes: 60 x 60 cm and 90 x 90 cm / 100% Silk
$47.00 – $79.90“Abstract Rose” Silk Scarf
$47.00 – $79.90 -
“Armenian Ceramics” Scarf
Jerusalem’s ancient Armenian community experienced a major increase in numbers as survivors of the Armenian genocide perpetrated by the government of the Ottoman Empire beginning in 1915 found refuge in Jerusalem’s Armenian Quarter. The industry is believed to have been started by refugees from Kütahya, a city in western Anatolia noted for its Iznik pottery. The tiles decorate many of the city’s most notable buildings, including the Rockefeller Museum, American Colony Hotel, and the House of the President of Israel.
David Ohannessian (1884–1953), who had established a pottery in Kütahya in 1907, is credited with establishing the Armenian ceramic craft industry in Jerusalem. In 1911 Ohannessian was commissioned with installing Kütahya tile in the Yorkshire home of Mark Sykes. In 1919 Ohannessian and his family fled the Armenian genocide, finding temporary refuge in Aleppo; they moved to Jerusalem when Sykes suggested that they might be able to replicate the broken and missing tiles on the Dome of the Rock, a building then in a decayed and neglected condition. Although the commission for the Dome of the Rock did not come through, the Ohannession pottery in Jerusalem succeeded, as did the Karakashian the painters and Balian the potters that Ohannessian brought with him from Kuttahya to help him with the project in 1919. After about 60 years new Armenian artists started to have their own studios.
In 2019 the Israel Museum mounted a special exhibition of Jerusalem pottery in its Rockefeller Museum branch location.$110.00“Armenian Ceramics” Scarf
$110.00 -
New Noravank
Available in two sizes 90X90, 60X60 100% Silk
$47.00 – $79.90New Noravank
$47.00 – $79.90 -