-
“Armenian Manuscripts” Scarf
Armenian illuminated manuscripts form a separate tradition, related to other forms of Medieval Armenian art, but also to the Byzantine tradition. The earliest surviving examples date from the Golden Age of Armenian art and literature in the 5th century. Early Armenian Illuminated manuscripts are remarkable for their festive designs to the Armenian culture; they make one feel the power of art and the universality of its language. The greatest Armenian miniaturist, Toros Roslin, lived in the 13th century.
The Matenadaran Institute in Yerevan has the largest collection of Armenian manuscripts, including the Mugni Gospels and Echmiadzin Gospels. The second largest collection of Armenian illuminated manuscripts is stored in the depository of St. James Cathedral, of the Holy Apostolic Church’s Patriarchate of Jerusalem. Other collections exist in the British Library, Bibliothèque nationale de France, and other large collections at the Mechitarist establishments in Venice and Vienna, as well as in the United States. The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) keeps an Armenian illuminated manuscript dating back to the 14th century among its collection of Armenian manuscripts, which is one of the largest in the world. They also have the manuscript of the Gladzor Gospels (cf. University of Gladzor).$50.00 – $110.00 -
-
“Cuneiform” Silk Scarf
In the mid-9th century BC, one of the most powerful states of the Ancient Near East, known as Urartu from Assyrian inscriptions, came down to the historic scene in the Armenian Highland. The Urartians called their country Biainili. It is mentioned as the Araratian Kingdom in the Bible.
Artefacts found, bear witness to a highly developed civilization of ancient Eastern type with a solid state system, literature, original ritual-religious system, prospering towns, crafts and arts. Urartu collapsed in the struggle against the Medians, Babylonians and Scythians in 585 BC. After the decline of the Urartian statehood, the kingdom of the Armenian Yervandids (Orontids) was formed on the same territory.
$90.00 -
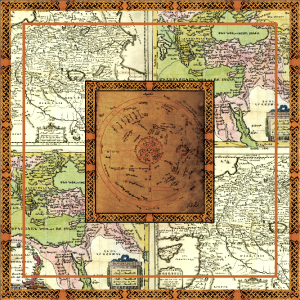
“Armenian Maps” Scarf
The oldest extant map of the world is depicted on a clay tablet. It is the Babylonian map found in Iraq, in 19 century. Now it is stored in the British Museum.
This Babylonian map of the World dates back to 6 century BC. In ancient Assyrian and Babylonian sources the kingdom of Ararat is referred to as Urartu. This name is mentioned on the world’s oldest map. Of the countries mentioned in this map, only Armenia still exists. All the other ones have disappeared from the world map.
https://www.armgeo.am/en/armenia-on-the-oldest-maps-of-the-world/$50.00 – $110.00 -
“Julfa Khachkar” Scarf
Inspired by the Armenian khachkars (cross stones) ruined by Azeris in Nakhichevan.
In 2005 the Azerbaijani authorities destroyed the Armenian cemetery in the city of Jugha in Nakhichevan with its thousands of valuable khachkars. They were displaced and broken by the use of construction equipment and thereby used as construction material, while the vacated area of the cemetery was turned into a military school. Thus, the Azerbaijani authorities have proven that they are capable of pursuing their policy of ethnic cleansing by destroying Armenian historical traces.$90.00 -
“Trchnagir” Alphabet
The Armenian alphabet was created in 405 AD.
One of the greatest marks of the Armenian identity is the Armenian language. The exact origins of the Armenian language, however, are a little bit obscure. Such is the case with many ancient languages. Serious scholarship starting from the 19th century has placed Armenian among the wider family of Indo-European languages, although it forms its own separate branch within that group. So the language does not have any close relatives today, even Indo-European ones, such as Spanish and Portuguese or Russian and Polish might be considered.Armenian is also unique in its writing system. The Armenians use their own alphabet which was, by tradition, created following the studies and meditations of a monk, Mesrop Mashtots, in the early 5th century AD. Christianity had already been accepted as the national religion for a hundred years in Armenia, but the Bible was not yet available in the native language. The tradition goes that the main motivation to come up with a separate Armenian alphabet was in order to translate the Bible in such a way that would be accessible and suitable for the language and the people.
Mesrop Mashtots – who has since been venerated as a saint, as the patron of teaching and learning for Armenians – accomplished the task in the year 405 AD, thus setting the stage for a rich trove of works of religion and history, science and philosophy, illuminated manuscripts, and published books in the millennium and a half that followed, continuing on today. A major road in the capital of Armenia, Yerevan, is named for Mashtots, and one end of it is the apt location for the Matenadaran, the national repository of manuscripts which also functions as a research institute and museum.
$110.00“Trchnagir” Alphabet
$110.00 -