Thermo Interstellar Blend
$255.00 – $500.00
INTERSTELLAR BLEND “THERMO” The Ultimate Fat Burning Formula & Glucose Disposal Agent
INTERSTELLAR BLEND “THERMO”
The Ultimate Fat Burning Formula & Glucose Disposal Agent
300 1/8 teaspoon servings per bag
DOSAGE:
A little more frequent is more effective than a lot all at once.
Start with 1/8 teaspoon in 2-4 oz of hot water
every 4-6 hours and adjust accordingly.
For OPTIMUM RESULTS to preserve muscle and burn fat take 1/8 to 1/4 teaspoon PREWORKOUT in FASTED STATE
- BENEFITS INCLUDE:
- GLUCONEOGENESIS INHIBITION. (STOPS MUSCLES FROM BEING ROBBED OF THEIR AMINO ACIDS TO PRODUCE GLUCOSE)
- INCREASED INSULIN SENSITIVITY THROUGH INSULIN MIMETICS AND INSULIN SENSITIZERS.
- ENHANCED SHUTTLING OF GLUCOSE INTO MUSCLES.
- LOWERED AND REGULATED BLOOD SUGAR.
- TARGETED REMOVAL OF STUBBORN SUBCUTANEOUS AND VISCERAL FAT.
- EFFICIENTLY DETERRING INSULIN RESISTANT INDUCED NEW FAT STORAGE.
- ENHANCED MENTAL FOCUS, ENERGY AND CLARITY.
- AMPK ACTIVATION.
- MTOR INHIBITION.
- DIABETIC AND PREDIABETIC PROTECTION WHEN COMBINED WITH LOW GLYCEMIC LOAD DIET.
Click on links below to in depth learn about each of the ingredients in this amazing one of a kind blend! Test your blood sugar before and after and see for yourself!

Coriolus Versicolor (Turkey Tail Mushroom)
- Macrophage-Stimulating Activity of Polysaccharides Extracted from Fruiting Bodies of Coriolus versicolor (Turkey Tail Mushroom)
- Beta‐glucans in higher fungi and their health effects
- A review of research on the protein-bound polysaccharide (polysaccharopeptide, PSP) from the mushroom Coriolus versicolor (Basidiomycetes: Polyporaceae)
- Coriolus versicolor polysaccharide peptide slows progression of advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- Polysaccharopeptides of Coriolus versicolor: physiological activity, uses, and production
- Antitumor effects of a refined polysaccharide peptide fraction isolated from Coriolus versicolor: in vitro and in vivo studies
- Separation, purification, and α-glucosidase inhibition of polysaccharides from Coriolus versicolor LH1 mycelia
- Hypoglycemic effects of exo-biopolymers produced by five different medicinal mushrooms in STZ-induced diabetic rats
- In vitro chemopreventive effects of plant polysaccharides (Aloe barbadensis Miller, Lentinus edodes, Ganoderma lucidum and Coriolus versicolor)
- Anti-tumor effect of Coriolus versicolor methanol extract against mouse B16 melanoma cells: in vitro and in vivo study
Mirabilis Jalapa (Ursolic Acid)
- Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of ethanolic extract of Mirabilis jalapa L. root on normal and diabetic mice
- Experimental diabetes treated with trigonelline: effect on β cell and pancreatic oxidative parameters
- Study on Hypoglycemic Effect of Mirabilis jalapa on Adrenergic Model Mice [J]
- Antiviral and Antiviroid Activity of MAP-Containing Extracts from Mirabilis jalapa Roots
- Antinociceptive activity of Mirabilis jalapa in mice
- In-vitro antioxidant potential of methanolic extracts of Mirabilis jalapa Linn
- Biochemical analysis of Cassia fistula aqueous extract and phytochemically synthesized gold nanoparticles as hypoglycemic treatment for diabetes mellitus
- GC/MS and LC/MS analysis, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of various solvent extracts from Mirabilis jalapa tubers
- Antinociceptive effect of Mirabilis jalapa on acute and chronic pain models in mice
- Pharmacological study of antispasmodic activity of Mirabilis jalapa Linn flowers
- Evaluation of antioxidant and wound healing effects of alcoholic and aqueous extract of Ocimum sanctum Linn in rats
- Antioxidant activity and lipid-lowering effect of essential oils extracted from Ocimum sanctum L. leaves in rats fed with a high cholesterol diet
- Antidiabetic effects of the different fractions of ethanolic extracts of Ocimum sanctum in normal and alloxan induced diabetic rats
- Hypoglycemic effect of Ocimum sanctum leaf extract in normal and streptozotocin diabetic rats.
- Ethanolic extract of Ocimum sanctum leaves partially attenuates streptozotocin-induced alterations in glycogen content and carbohydrate metabolism in rats
- Effect of Ocimum sanctum leaf powder on blood lipoproteins, glycated proteins and total amino acids in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
- Ocimum sanctum leaf extracts stimulate insulin secretion from perfused pancreas, isolated islets and clonal pancreatic β-cells
- Antidiabetic, antihypercholesterolaemic and antioxidant effect of Ocimum sanctum (Linn) seed oil
- Randomized placebo-controlled, single blind trial of holy basil leaves in patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
- Evaluation of hypoglycemic and antioxidant effect ofOcimum sanctum

- Naringenin prevents obesity, hepatic steatosis, and glucose intolerance in male mice independent of fibroblast growth factor 21
- Naringenin prevents dyslipidemia, apolipoprotein B overproduction, and hyperinsulinemia in LDL receptor–null mice with diet-induced insulin resistance
- Naringenin suppresses macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue in an early phase of high-fat diet-induced obesity
- DNA-protective effects of quercetin or naringenin in alloxan-induced diabetic mice
- Anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects of naringenin in diabetic mice
- Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes
- Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant effects of a flavanone, naringenin, in streptozotocin–nicotinamide-induced experimental diabetic rats
- Participation of antioxidant and cholinergic system in protective effect of naringenin against type-2 diabetes-induced memory dysfunction in rats
- Effect of citrus flavonoids on lipid metabolism and glucose-regulating enzyme mRNA levels in type-2 diabetic mice
- Inhibition of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein expression and apolipoprotein B100 secretion by the citrus flavonoid naringenin and by insulin involves activation

Oroxylum Indicum (Indian trumpet flower)
- Oroxylin A, a constituent of Oroxylum indicum inhibits adipogenesis and induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1 cells
- Modulation of liver function, antioxidant responses, insulin resistance and glucose transport by Oroxylum indicum stem bark in STZ induced diabetic rats
- Screening of six Ayurvedic medicinal plants for anti-obesity potential: An investigation on bioactive constituents from Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz bark
- Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz, an important Asian traditional medicine: from traditional uses to scientific data for its commercial exploitation
- Investigation of the anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of ethanol extract of stem bark of Sonapatha Oroxylum indicum in vivo
- Oroxin A from Oroxylum indicum prevents the progression from prediabetes to diabetes in streptozotocin and high-fat diet induced mice
- Evaluation of antidiabetic and nephroprotective activity of Oroxylum indicum L Kurz and Quercus infectoria G Olivier
- Protective effect of aqueous extract of Oroxylum indicum Linn.(root bark) against DNBS-induced colitis in rats
- Antimicrobial and antiinflammatory activities of extracts and constituents of Oroxylum indicum (L.) Vent
- In vitro antioxidant activity from leaves of Oroxylum indicum (L.) Vent.-A North Indian highly threatened and vulnerable medicinal plant

Rauwolfia Serpentina(Indian Snakeroot)
- On the use of Rauwolfia serpentina in high blood pressure
- Methanolic root extract of Rauwolfia serpentina benth improves the glycemic, antiatherogenic, and cardioprotective indices in alloxan-induced diabetic mice
- Hypertension Treated with Rauwolfia canescens A Comparison with Rauwolfia serpentina
- Hypoglycaemic and hypolipidemic activities of Rauwolfia serpentina in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.
- A clinical trial of Rauwolfia serpentina in essential hypertension
- Phytochemical based strategies for pathogen control and antioxidant capacities of Rauwolfia serpentina extracts
- Methanolic root extract of Rauwolfia serpentina improves the glucose tolerance in wister mice
- Rauwolfia serpentina in the treatment of high blood pressure: a review of the literature
- Prospecting for novel plant-derived molecules of Rauvolfia serpentina as inhibitors of Aldose Reductase, a potent drug target for diabetes
- Rauwolfia serpentina in essential hypertension
- Obesity and thermogenesis related to the consumption of caffeine, ephedrine, capsaicin, and green tea
- Effects of capsaicin-containing yellow curry sauce on sympathetic nervous system activity and diet-induced thermogenesis in lean and obese young women
- Dietary capsaicin reduces obesity‐induced insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in obese mice fed a high‐fat diet
- Effect of treatment with capsaicin on daily activities of patients with painful diabetic neuropathy
- Treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy with topical capsaicin. A multicenter, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study
- Topical capsaicin in painful diabetic neuropathy: effect on sensory function
- Topical capsaicin in painful diabetic neuropathy: controlled study with long-term follow-up
- The effect of cannabinoids on capsaicin-evoked calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) release from the isolated paw skin of diabetic and non-diabetic rats
- A double-blind comparison of topical capsaicin and oral amitriptyline in painful diabetic neuropathy.
- Influence of dietary capsaicin and onion on the metabolic abnormalities associated with streptozotocin induced diabetes mellitus

Gynostemma (The Herb of Immortality)
- Anti-hyperlipidemic and hypoglycemic effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in the Zucker fatty rat
- Antiobesity effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract (actiponin): A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial
- Potential Hypoglycemic Effect of an Ethanol Extract of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in C57BL/KsJ-db/db Mice
- Antidiabetic effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum tea in randomly assigned type 2 diabetic patients
- Antidiabetic effects of add-on Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract therapy with sulfonylureas in type 2 diabetic patients
- Gynostemma pentaphyllum Tea Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- A novel insulin-releasing substance, phanoside, from the plant Gynostemma pentaphyllum
- Hypoglycemic effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins by enhancing the Nrf2 signaling pathway in STZ-inducing diabetic rats
- Heat-processed Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract improves obesity in ob/ob mice by activating AMP-activated protein kinase
- Effects of obesity on functional capacity

Rosa Canina (Trans-Tiliroside)
- Potent anti-obese principle from Rosa canina: structural requirements and mode of action of trans-tiliroside
- Effects of rose hip intake on risk markers of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over investigation in obese
- Rosehip extract inhibits lipid accumulation in white adipose tissue by suppressing the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- Antidiabetic effect and antioxidant potential of Rosa canina fruits
- In vivo anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity of the crude extract and fractions from Rosa canina L. fruits
- Rosa canina extracts have antiproliferative and antioxidant effects on caco-2 human colon cancer
- Effects of Rosa canina L. fruit on glycemia and lipid profile in type 2 diabetic patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
- Rose hip exerts antidiabetic effects via a mechanism involving downregulation of the hepatic lipogenic program
- Anti‐prediabetic effect of rose hip (Rosa canina) extract in spontaneously diabetic Torii rats
- Rosehip: an evidence based herbal medicine for inflammation and arthritis

Galega Officinalis (botanical version of Metformin)
- Novel weight‐reducing activity of Galega officinalis in mice
- A systematic review of the efficacy and safety of herbal medicines used in the treatment of obesity
- Administration of Galega officinalis in experimental and clinical investigations; a narrative review
- Alleviation of salt stress of symbiotic Galega officinalis L. (goat’s rue) by co-inoculation of Rhizobium with root-colonizing Pseudomonas
- Natural products in anti-obesity therapy
- Effect of Fabaceae (Galega Officinalis L.) consumption on levels of blood glucose, lipids and lipoproteins in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Anti-diabetic potential and Indian medicinal plants
- Antiplatelet Aggregation Activity of a Fraction Isolated from Galega officinalis L.
- The alkaloid-free fraction from Galega Officinalis extract prevents oxidative stress under experimental diabetes mellitus
- Cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of four different extracts of Galega officinalis L (Goat’s rue)
- Recent findings of green tea extract AR25 (Exolise) and its activity for the treatment of obesity
- Effect of green tea extract on obese women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
- Efficacy of a green tea extract rich in catechin polyphenols and caffeine in increasing 24-h energy expenditure and fat oxidation in humans
- Effects of green tea and EGCG on cardiovascular and metabolic health
- Assessment of DNA damage and lipid peroxidation in diabetic mice: effects of propolis and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)
- Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) attenuates high glucose‐induced insulin signaling blockade in human hepG2 hepatoma cells
- Effect of green tea on blood glucose levels and serum proteomic patterns in diabetic (db/db) mice and on glucose metabolism in healthy humans
- Epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) protects the insulin sensitivity in rat L6 muscle cells exposed to dexamethasone condition
- Protective effects of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in mice
- Effects of oral consumption of the green tea polyphenol EGCG in a murine model for human Sjogren’s syndrome, an autoimmune disease

- Calorie restriction-like effects of 30 days of resveratrol supplementation on energy metabolism and metabolic profile in obese humans
- Resveratrol exerts anti-obesity effects via mechanisms involving down-regulation of adipogenic and inflammatory processes in mice
- Long-term resveratrol administration reduces metabolic disturbances and lowers blood pressure in obese Zucker rats
- Resveratrol improves insulin sensitivity, reduces oxidative stress and activates the Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic patients
- Resveratrol, a red wine antioxidant, possesses an insulin-like effect in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- AMP-activated protein kinase–deficient mice are resistant to the metabolic effects of resveratrol
- Effect of insulin and its combination with resveratrol or curcumin in attenuation of diabetic neuropathic pain: participation of nitric oxide and TNF‐alpha
- Resveratrol alleviates cardiac dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetes: Role of nitric oxide, thioredoxin, and heme oxygenase
- Anti‐diabetic effects of resveratrol
- Effects of resveratrol on nerve functions, oxidative stress and DNA fragmentation in experimental diabetic neuropathy
- Effects of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) and Terminalia arjuna (Arjuna) on physical performance and cardiorespiratory endurance in healthy young
- Effect of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) Root Powder Supplementation in Treatment of Hypertension
- Body weight management in adults under chronic stress through treatment with Ashwagandha root extract: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
- Hypoglycaemic and hypolipidaemic effects of Withania somnifera root and leaf extracts on alloxan-induced diabetic rats
- Effect of dietary intake ashwagandha roots powder on the levels of sex hormones in the diabetic and non-diabetic male rats
- Effect of Withania somnifera on Insulin Sensitivity in Non‐Insulin‐Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Rats
- Effect of withania somnifera on levels of sex hormones in the diabetic male rats
- The effect of chronic oral administration of Withania somnifera root on learning and memory in diabetic rats using passive avoidance test
- Reverse Ayurvedic pharmacology of Ashwagandha as an adaptogenic anti-diabetic plant: a pilot study
- The effect of oral administration of Withania somnifera root on formalin-induced pain in diabetic rats
- Effects of ingested turmeric oleoresin on glucose and lipid metabolisms in obese diabetic mice: a DNA microarray study
- Effects of fermented turmeric extracts on the obesity in rats fed a high-fat diet
- Curcumin inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and angiogenesis and obesity in C57/BL mice
- Modulatory effects of garlic, ginger, turmeric and their mixture on hyperglycaemia, dyslipidaemia and oxidative stress in streptozotocin–nicotinamide diabetic rats
- Curcumin, the active principle of turmeric (Curcuma longa), ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in rats
- Curcuminoids and Sesquiterpenoids in Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) Suppress an Increase in Blood Glucose Level in Type 2 Diabetic KK-Ay Mice
- Hypolipidemic action of curcumin, the active principle of turmeric (Curcuma longa) in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats
- Efficacy of turmeric on blood sugar and polyol pathway in diabetic albino rats
- Effect of turmeric and curcumin on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat
- Curcumin and turmeric delay streptozotocin-induced diabetic cataract in rats

Bioperine
- Effect of piperine in the regulation of obesity-induced dyslipidemia in high-fat diet rats
- Piperine, an active principle from Piper nigrum, modulates hormonal and apolipoprotein profiles in hyperlipidemic rats
- LIPID‐LOWERING EFFICACY OF PIPERINE FROM PIPER NIGRUM L. IN HIGH‐FAT DIET AND ANTITHYROID DRUG‐INDUCED HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIC
- Effects of piperine on antioxidant pathways in tissues from normal and streptozotocin‐induced diabetic rats
- Evaluation of the effect of piperine per se on blood glucose level in alloxan-induced diabetic mice
- Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of curcuminoid-piperine combination in subjects with metabolic syndrome
- Piperine, a natural bioenhancer, nullifies the antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of curcumin in streptozotocin-diabetic rats
- Protective effect of piperine on benzo (a) pyrene-induced lung carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice
- Piperine reverses high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in mice
- Effects of curcuminoids-piperine combination on systemic oxidative stress, clinical symptoms
- Effects and action mechanisms of berberine and Rhizoma coptidis on gut microbes and obesity in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice
- Structural changes of gut microbiota during berberine-mediated prevention of obesity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed rats
- Berberine improves lipid dysregulation in obesity by controlling central and peripheral AMPK activity
- Lipid-lowering effect of berberine in human subjects and rats
- Berberine inhibits adipogenesis in high-fat diet-induced obesity mice
- Berberine suppresses proinflammatory responses through AMPK activation in macrophages
- Modulating gut microbiota as an anti-diabetic mechanism of berberine
- Berberine improves glucose metabolism through induction of glycolysis
- Insulin sensitizing and insulinotropic action of berberine from Cortidis rhizoma
- Anti-diabetic effects of cinnamaldehyde and berberine and their impacts on retinol-binding protein 4 expression in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus

Pausinystalia Johimbe (stubborn fat alpha blocker)
- Plasma catecholamine levels and lipid mobilization induced by yohimbine in obese and non-obese women.
- Cardiovascular effects of ephedrine, caffeine and yohimbine measured by thoracic electrical bioimpedance in obese women
- Yohimbine: the effects on body composition and exercise performance in soccer players
- Yohimbe Alkaloids–General Discussion
- The histological effects of mixed diet containing Pausinystalia yohimbe ground stem bark on the kidney of adult Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus)
- Noradrenergic function in generalized anxiety disorder: effects of yohimbine in healthy subjects and patients with generalized anxiety disorder
- Yohimbine for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Cameroonian medicinal plants: pharmacology and derived natural products
- Effects of methanolic extract of Pausinystalia yohimbe bark on blood glucose level in normal fasting rats
- Effects of methanolic extract of yohimbe bark (Pausinystalia yohimbe) on isolated rabbit aortic strip and rat uterus

Green Coffee Bean Extract (Chlorogenic Acid)
- The effect of chlorogenic acid enriched coffee on glucose absorption in healthy volunteers and its effect on body mass when used long-term in overweight and obese
- Chlorogenic acid exhibits anti-obesity property and improves lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced-obese mice
- Chlorogenic acid modifies plasma and liver concentrations of: cholesterol, triacylglycerol, and minerals in (fa/fa) Zucker rats
- Coffee acutely modifies gastrointestinal hormone secretion and glucose tolerance in humans: glycemic effects of chlorogenic acid and caffeine
- Acute effects of decaffeinated coffee and the major coffee components chlorogenic acid and trigonelline on glucose tolerance
- A chlorogenic acid-induced increase in GLP-1 production may mediate the impact of heavy coffee consumption on diabetes risk
- Chlorogenic acid stimulates glucose transport in skeletal muscle via AMPK activation: a contributor to the beneficial effects of coffee on diabetes
- Anti-diabetic and anti-lipidemic effects of chlorogenic acid are mediated by ampk activation
- Coffee consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Chlorogenic acid and rutin play a major role in the in vivo anti-diabetic activity of Morus alba leaf extract on type II diabetic rats

- Body composition and hormonal adaptations associated with forskolin consumption in overweight and obese men
- The antihypertensive and positive inotropic diterpene forskolin: effects of structural modifications on its activity
- Antagonism of forskolin effects by adenosine in isolated hearts and ventricular myocytes
- Effect of chronic administration of forskolin on glycemia and oxidative stress in rats with and without experimental diabetes
- Insulin and glucagon releasing activity of coleonol (forskolin) and its effect on blood glucose level in normal and alloxan diabetic rats
- Insulin biosynthesis in HIT cells: effects of glucose, forskolin, IBMX, and dexamethasone
- Direct anesthetic-like effects of forskolin on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of PC12 cells.
- The ionic, electrical, and secretory effects of endogenous cyclic adenosine monophosphate in mouse pancreatic B cells: studies with forskolin
- The effects of forskolin and rolipram on cAMP, cGMP and free fatty acid levels in diet induced obesity
- Forskolin effects on the voltage-gated K+ conductance of human T cells
- Pharmacological stimulation of NADH oxidation ameliorates obesity and related phenotypes in mice
- Regulation of leaf senescence by cytokinin, sugars, and light: effects on NADH-dependent hydroxypyruvate reductase
- Therapeutic effects of oral NADH on the symptoms of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome
- Effects of cytosolic NADH/NAD+ levels on sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release in permeabilized rat ventricular myocytes
- Effects of glucose and PaO2 modulation on cortical intracellular acidosis, NADH redox state, and infarction in the ischemic penumbra
- Low-potential stable NADH detection at carbon-nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrodes
- Effects of NADH and NADPH on superoxide levels and cerebral vascular tone
- Kinetic experiments on the synergistic effect of NADH on microsomal drug oxidation
- Effects of base on oxidation of an NADH model compound by iron (III) complexes and tetracyanoethylene
- Evidence that metformin exerts its anti-diabetic effects through inhibition of complex 1 of the mitochondrial respiratory chain
- Efficacy of Nigella sativa on serum free testosterone and metabolic disturbances in central obese male.
- Multiple molecular targets underlie the antidiabetic effect of Nigella sativa seed extract in skeletal muscle, adipocyte and liver cells
- Antihypertensive effect of Nigella sativa seed extract in patients with mild hypertension
- Effect of Nigella sativa on glucose concentration, lipid peroxidation, anti‐oxidant defence system and liver damage in experimentally‐induced diabetic rabbits
- Hypoglycemic effects of the volatile oil of Nigella sativa seeds
- Effects of Nigella sativa on oxidative stress and β‐cell damage in streptozotocin‐induced diabetic rats
- Biochemical effects of Nigella sativa L seeds in diabetic rats
- Mechanisms of the hypoglycaemic and immunopotentiating effects of Nigella sativa L. oil in streptozotocin-induced diabetic hamsters
- Isulinotropic properties of Nigella sativa oil in Streptozotocin plus Nicotinamide diabetic hamster
- Partial regeneration/proliferation of the β-cells in the Islets of Langerhans by Nigella sativa L. in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats

Hoodia Gordonii (Queen of the Namib)
- Effects of 15-d repeated consumption of Hoodia gordonii purified extract on safety, ad libitum energy intake, and body weight in healthy, overweight women
- Hoodia gordonii in the treatment of obesity: A review
- Metabolic effect of short term administration of Hoodia gordonii, an herbal appetite suppressant
- Hoodia gordonii: a natural appetite suppressant
- Indigenous use of Hoodia gordonii and appetite suppression
- Complementary and alternative medicine for the treatment of obesity: a critical review
- Sympathomimetic activity of a Hoodia gordonii product: a possible mechanism of cardiovascular side effects
- Hoodia gordonii extract targets both adipose and muscle tissue to achieve weight loss in rats
- Metabolic response of short term calorie restriction and supplementation with Hoodia gordonii
- In vitro transport of the steroidal glycoside P57 from Hoodia gordonii across excised porcine intestinal and buccal tissue
- Fucoxanthin from edible seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida, shows antiobesity effect through UCP1 expression in white adipose tissues
- Anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects of fucoxanthin on diet-induced obesity conditions in a murine model
- Effect of medium-chain triacylglycerols on anti-obesity effect of fucoxanthin
- Fucoxanthin and its metabolite, fucoxanthinol, suppress adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells
- Dietary Combination of Fucoxanthin and Fish Oil Attenuates the Weight Gain of White Adipose Tissue and Decreases Blood Glucose in Obese/Diabetic KK-Ay Mice
- Anti‐obese property of fucoxanthin is partly mediated by altering lipid‐regulating enzymes and uncoupling proteins of visceral adipose tissue in mice
- Fucoxanthin regulates adipocytokine mRNA expression in white adipose tissue of diabetic/obese KK-Ay mice
- Fucoxanthin and fucoxanthinol enhance the amount of docosahexaenoic acid in the liver of KKAy obese/diabetic mice
- Effects of dietary fucoxanthin on cholesterol metabolism in diabetic/obese KK-A y mice
- The carotenoid fucoxanthin from brown seaweed affects obesity

Bitter Melon(momordica charantia)
- Effects of Momordica charantia on insulin resistance and visceral obesity in mice on high-fat diet
- Antihyperglycemic effects of three extracts from Momordica charantia
- The effect of Momordica charantia and Mucuna pruriens in experimental diabetes and their effect on key metabolic enzymes involved in carbohydrate metabolism
- Bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.) inhibits adipocyte hypertrophy and down regulates lipogenic gene expression in adipose tissue of diet-induced obese rats
- Effects of Momordica charantia powder on serum glucose levels and various lipid parameters in rats fed with cholesterol-free and cholesterol-enriched diets
- Anti-diabetic and hypoglycaemic effects of Momordica charantia (bitter melon): a mini review
- Inhibition of increases in blood glucose and serum neutral fat by Momordica charantia saponin fraction
- An experimental evaluation of the antidiabetic and antilipidemic properties of a standardized Momordica charantia fruit extract
- The insulin-releasing activity of the tropical plant momordica charantia.
- Antidiabetic Potentials of Momordica charantia: Multiple Mechanisms Behind the Effects

Banaba Leaf (Lagerstroemia speciosa)
- Antiobesity activity of extracts from Lagerstroemia speciosa L. leaves on female KK-Ay mice
- Antidiabetes and anti-obesity activity of Lagerstroemia speciosa
- Hypoglycemic activity of Lagerstroemia speciosa L. extract on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat: Underlying mechanism of action
- An extract of Lagerstroemia speciosa L. has insulin-like glucose uptake–stimulatory and adipocyte differentiation–inhibitory activities in 3T3-L1 cells
- Antidiabetic activity of a standardized extract (Glucosol™) from Lagerstroemia speciosa leaves in type II diabetics: A dose-dependence study
- Active Compounds from Lagerstroemia speciosa, Insulin-like Glucose Uptake-Stimulatory/Inhibitory and Adipocyte Differentiation-Inhibitory Activities in 3T3-L1 Cells
- Hypoglycemic effect of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) Pers. on alloxan-induced diabetic mice
- The hypoglycemic effect of water extract from leaves of Lagerstroemia speciosa L. in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
- Lagerstroemia speciosa extract inhibit TNF-induced activation of nuclear factor-κB in rat cardiomyocyte H9c2 cells
- Hypoglycemic effect of extracts from Lagerstroemia speciosa L. leaves in genetically diabetic KK-AY mice

Gymnema Sylvestre (Miracle Fruit)
- Antihyperglycemic Effects of Gymnemic Acid IV, a Compound Derived from Gymnema sylvestre Leaves in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Mice
- Comparative effects of chromium, vanadium and Gymnema sylvestre on sugar-induced blood pressure elevations in SHR
- Evaluation of antiobesity and cardioprotective effect of Gymnema sylvestre extract in murine model
- Antidiabetic effect of a leaf extract from Gymnema sylvestre in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients
- Possible regeneration of the islets of Langerhans in streptozotocin-diabetic rats given Gymnema sylvestre leaf extracts
- Use of Gymnema sylvestre leaf extract in the control of blood glucose in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
- Gymnema sylvestre stimulates insulin release in vitro by increased membrane permeability
- Enzyme changes and glucose utilisation in diabetic rabbits: the effect of Gymnema sylvestre, R. Br.
- Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic activity of Gymnema sylvestre in alloxan induced diabetic rats
- In vitro callus and in vivo leaf extract of Gymnema sylvestre stimulate β-cells regeneration and anti-diabetic activity in Wistar rats
- Effects of exercise training and antioxidant R-ALA on glucose transport in insulin-sensitive rat skeletal muscle
- Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential
- α-Lipoic acid: a multifunctional antioxidant that improves insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Alpha-lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant
- Antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a 7-month multicenter randomized controlled trial (ALADIN III Study). ALADIN III Study Group. Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Diabetic
- Effects of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on peripheral nerve conduction, blood flow, energy metabolism, and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic neuropathy
- alpha-Lipoic acid treatment decreases serum lactate and pyruvate concentrations and improves glucose effectiveness in lean and obese patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Alpha-lipoic acid: antioxidant potency against lipid peroxidation of neural tissues in vitro and implications for diabetic neuropathy
- Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on microcirculation in patients with peripheral diabetic neuropathy
- Alpha-lipoic acid: effect on glucose uptake, sorbitol pathway, and energy metabolism in experimental diabetic neuropathy.

Cissus Quadrangularis (Asthisamharaka)
- The effect of Cissus quadrangularis (CQR-300) and a Cissus formulation (CORE) on obesity and obesity-induced oxidative stress
- The use of a Cissus quadrangularis/Irvingia gabonensis combination in the management of weight loss: a double-blind placebo-controlled study
- The use of a Cissus quadrangularis formulation in the management of weight loss and metabolic syndrome
- Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Cissus quadrangularis L.
- Pharmacological actions of Cassia auriculata L. and Cissus quadrangularis Wall: A short review
- Hypoglycemic and anti-lipemic effects of the aqueous extract from Cissus sicyoides
- Cissus quadrangularis stem alleviates insulin resistance, oxidative injury and fatty liver disease in rats fed high fat plus fructose diet
- Beneficial effect of Cissus quadrangularis Linn. on osteopenia associated with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus in male Wistar rats
- Evaluation of the antidiabetic and antibacterial activity of Cissus sicyoides
- Cissus quadrangularis extract attenuates hyperglycaemia-mediated oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Effect of sesamin supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in women with rheumatoid arthritis
- The sesame lignan sesamin attenuates vascular dysfunction in streptozotocin diabetic rats: involvement of nitric oxide and oxidative stress
- Sesame oil exhibits synergistic effect with anti-diabetic medication in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Antihypertensive effect of sesamin. IV. Inhibition of vascular superoxide production by sesamin
- Quercetin and sesamin protect neuronal PC12 cells from high-glucose-induced oxidation, nitrosative stress, and apoptosis
- Effects of vitamin E and sesamin on hypertension and cerebral thrombogenesis in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats
- Hypoglycaemic and hypolipidaemic activities of sesamin from sesame meal and its ability to ameliorate insulin resistance in KK‐Ay mice
- Effects of sesamin on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced NIT-1 pancreatic β-cell damage
- EFFECTS OF VITAMIN E AND SESAMIN ON HYPERTENSION AND CEREBRAL THROMBOGENESIS IN STROKE‐PRONE SPONTANEOUSLY HYPERTENSIVE
- Preventive effect of sesame seed cake on hyperglycemia and obesity against high fructose-diet induced Type 2 diabetes in rats
- Callophyllis japonica extract improves high-fat diet-induced obesity and inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells
- Anti-inflammatory effect of polyphenol-rich extract from the red alga Callophyllis japonica in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages
- Anti-obesity effect of Solidago virgaaurea extract in high-fat diet-fed SD rat
- Antioxidant activity of ethanol extract of Callophyllis japonica
- Investigation of the antiasthmatic properties of ethanol extract of Callophyllis japonica in mice
- Antioxidants from macroalgae: potential applications in human health and nutrition
- The radioprotective effects of the hexane and ethyl acetate extracts of Callophyllis japonica in mice that undergo whole body irradiation
- Effects of Callophyllis japonica powder on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats
- A comparative study of radioprotection with Callophyllis japonica extract and amifostine against lethal whole body gamma irradiation in mice
- Immunomodulatory Effects of Callophyllis japonica Ethanol Extract on Dendritic Cells
- Citrus bioactive phenolics: Role in the obesity treatment
- Citrus aurantium flavonoids inhibit adipogenesis through the Akt signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 cells
- Tangeretin stimulates glucose uptake via regulation of AMPK signaling pathways in C2C12 myotubes and improves glucose tolerance in high-fat diet-induced obese
- Effect of tangeretin, a polymethoxylated flavone on glucose metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Regulation of adipocytokine secretion and adipocyte hypertrophy by polymethoxyflavonoids, nobiletin and tangeretin
- Modulation of HepG2 cell net apolipoprotein B secretion by the citrus polymethoxyflavone, tangeretin
- Phenolic compositions and antioxidant capacities of Chinese wild mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco) fruits
- Studies on preparation of ready to serve mandarin (Citrus reticulata) diet drink
- Polymethoxylated, C-and O-glycosyl flavonoids in tangelo (Citrus reticulata× Citrus paradisi) juice and their influence on antioxidant properties
- Polymethoxyflavonoids tangeretin and nobiletin increase glucose uptake in murine adipocytes
- Arctigenin Inhibits Adipogenesis by Inducing AMPK Activation and Reduces Weight Gain in High‐Fat Diet‐Induced Obese Mice
- Arctigenin protects cultured cortical neurons from glutamate‐induced neurodegeneration by binding to kainate receptor
- Tumor specific cytotoxicity of arctigenin isolated from herbal plant Arctium lappa L.
- Arctigenin efficiently enhanced sedentary mice treadmill endurance
- Comparative pharmacokinetics of arctigenin in normal and type 2 diabetic rats after oral and intravenous administration
- In vitro anti-inflammatory effects of arctigenin, a lignan from Arctium lappa L., through inhibition on iNOS pathway
- Immunomodulatory Effect of Arctigenin, a Lignan Compound, on Tumour Necrosis Factor‐α and Nitric Oxide Production, and Lymphocyte Proliferation
- Therapeutic effect of arctiin and arctigenin in immunocompetent and immunocompromised mice infected with influenza A virus
- Antiproliferative effect of arctigenin and arctiin
- Arctigenin, a phenylpropanoid dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, inhibits MAP kinases and AP-1 activation via potent MKK inhibition: the role in TNF-α inhibition

Citrus Aurantium (Bitter Orange)
- Metabolic and physiological effects of ingesting extracts of bitter orange, green tea and guarana at rest and during treadmill walking in overweight males
- Citrus aurantium and synephrine alkaloids in the treatment of overweight and obesity: an update
- A review of the human clinical studies involving Citrus aurantium (bitter orange) extract and its primary protoalkaloid p-synephrine
- Increase in the thermic effect of food in women by adrenergic amines extracted from citrus aurantium
- Citrus aurantium as a thermogenic, weight-reduction replacement for ephedra: an overview.
- Tissue lipid lowering-effect of a traditional Nigerian anti-diabetic infusion of Rauwolfia vomitoria foilage and Citrus aurantium fruit
- Effects of Citrus aurantium extract, caffeine, and St. John’s wort on body fat loss, lipid levels, and mood states in overweight healthy adults
- Thermic effect of Citrus aurantium in obese subjects
- Anxiolytic and sedative effects of extracts and essential oil from Citrus aurantium L.
- Antiobesity and cardiovascular toxic effects of Citrus aurantium extracts in the rat: a preliminary report

Pyrroloquinoline Quinone(PQQ) (Natto)
- Altering pyrroloquinoline quinone nutritional status modulates mitochondrial, lipid, and energy metabolism in rats
- Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) producing Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) alleviates age associated oxidative stress and hyperlipidemia
- Pyrroloquinoline quinone stimulates epithelial cell proliferation by activating epidermal growth factor receptor through redox cycling
- Potential physiological importance of pyrroloquinoline quinone
- Pyrroloquinoline quinone, a novel protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitor, activates insulin signaling in C2C12 myotubes and improves impaired glucose
- Effects of dietary pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium on growth, carcass characteristics, redox status, and mitochondria metabolism in broilers
- Early PQQ supplementation has persistent long-term protective effects on developmental programming of hepatic lipotoxicity and inflammation in obese mice
- Pyrroloquinoline quinone ameliorates oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in the brain of streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
- Pyrroloquinoline quinone stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis through CREB phosphorylation and increased PGC-1α expression
- Pyrroloquinoline quinone prevents developmental programming of microbial dysbiosis and macrophage polarization to attenuate liver fibrosis in offspring of obese

Hesperidin (Citrus Cinsinensis osbeck)
- The hypoglycemic effects of hesperidin and naringin are partly mediated by hepatic glucose-regulating enzymes in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice
- Effects of hesperidin on the progression of hypercholesterolemia and fatty liver induced by high-cholesterol diet in rats
- Oral intake of a combination of glucosyl hesperidin and caffeine elicits an anti-obesity effect in healthy, moderately obese subjects: a randomized double-blind
- Chemopreventive effects of diosmin and hesperidin on N‐butyl‐N‐(4‐hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine‐induced urinary‐bladder carcinogenesis in male ICR mice
- Citrus polyphenol hesperidin stimulates production of nitric oxide in endothelial cells while improving endothelial function and reducing inflammatory markers
- Dietary hesperidin exerts hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects in streptozotocin-induced marginal type 1 diabetic rats
- Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of hesperidin and cyclodextrin-clathrated hesperetin in Goto-Kakizaki rats with type 2 diabetes
- Hesperidin prevents retinal and plasma abnormalities in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Antidiabetic effects of hesperidin and naringin in type 2 diabetic rats.
- Molecular mechanisms behind the biological effects of hesperidin and hesperetin for the prevention of cancer and cardiovascular diseases
- DM235 (sunifiram): a novel nootropic with potential as a cognitive enhancer
- AMPA-receptor activation is involved in the antiamnesic effect of DM 232 (unifiram) and DM 235 (sunifiram)
- Structure–activity relationship studies on unifiram (DM232) and sunifiram (DM235), two novel and potent cognition enhancing drugs
- Novel nootropic drug sunifiram improves cognitive deficits via CaM kinase II and protein kinase C activation in olfactory bulbectomized mice
- Novel nootropic drug sunifiram enhances hippocampal synaptic efficacy via glycine‐binding site of N‐methyl‐D‐aspartate receptor
- Design, synthesis and preliminary pharmacological evaluation of new analogues of DM232 (unifiram) and DM235 (sunifiram) as cognition modulators
- Design, synthesis and nootropic activity of new analogues of sunifiram and sapunifiram, two potent cognition-enhancers

- Antidiabetic effect of green rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) extract in cultured cells and type 2 diabetic model KK-Ay mice
- Hypoglycemic effect of aspalathin, a rooibos tea component from Aspalathus linearis, in type 2 diabetic model db/db mice
- Rooibos tea (Aspalathus linearis) partially prevents oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- The cardioprotective effect of an aqueous extract of fermented rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) on cultured cardiomyocytes derived from diabetic rats
- Acute assessment of an aspalathin-enriched green rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) extract with hypoglycemic potential
- Effects of rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) on oxidative stress and biochemical parameters in adults at risk for cardiovascular disease
- Ameliorative effect of aspalathin from rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) on acute oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans
- Aspalathin and Nothofagin from Rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) Inhibits High Glucose-Induced Inflammation In Vitro and In Vivo
- Modulation of antioxidant status in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male wistar rats following intake of red palm oil and/or rooibos
- Effects of rooibos tea extract on antigen-specific antibody production and cytokine generation in vitro and in vivo
- An evaluation of the hypolipidemic effect of an extract of Hibiscus Sabdariffa leaves in hyperlipidemic Indians: a double blind, placebo controlled trial
- Development of functional beverages from blends of Hibiscus sabdariffa extract and selected fruit juices for optimal antioxidant properties
- Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa on obesity in MSG mice
- Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa extract powder and preventive treatment (diet) on the lipid profiles of patients with metabolic syndrome (MeSy)
- The effects of sour tea (Hibiscus sabdariffa) on hypertension in patients with type II diabetes
- Effect of Hibiscus rosa sinensis Linn. ethanol flower extract on blood glucose and lipid profile in streptozotocin induced diabetes in rats
- Hibiscus extract inhibits the lipid droplet accumulation and adipogenic transcription factors expression of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes
- Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Dried Calyx Ethanol Extract on Fat Absorption-Excretion, and Body Weight Implication in Rats
- Lipids lowering effect of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis flower petals on monosodium glutamate (MSG) induced obese rats
- Inhibition of angiotensin convertin enzyme (ACE) activity by the anthocyanins delphinidin-and cyanidin-3-O-sambubiosides from Hibiscus sabdariffa

Evodia Rutaccarpa Fruit Extract
- Capsaicin-like anti-obese activities of evodiamine from fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa, a vanilloid receptor agonist
- Anti-inflammatory and anti-infectious effects of Evodia rutaecarpa (Wuzhuyu) and its major bioactive components
- Evodia alkaloids suppress gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis by activating the constitutive androstane receptor
- Evodiamine: a novel anti-cancer alkaloid from Evodia rutaecarpa
- Effect of herbal Ephedra sinica and Evodia rutaecarpa on body composition and resting metabolic rate
- Inhibitory effect of rhetsinine isolated from Evodia rutaecarpa on aldose reductase activity
- The nociceptive and anti-nociceptive effects of evodiamine from fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa in mice
- The positive inotropic and chronotropic effects of evodiamine and rutaecarpine, indoloquinazoline alkaloids isolated from the fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa
- Anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of the ethanol extract of Evodia rutaecarpa and its bioactive components on neutrophils and microglial cells
- Novel anticholinesterase and antiamnesic activities of dehydroevodiamine, a constituent of Evodia rutaecarpa
- Anti-obesity effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate, orange peel extract, black tea extract, caffeine and their combinations in a mouse model
- Antiobesity Effects of Chinese Black Tea (Pu‐erh Tea) Extract and Gallic Acid
- Antihypercholesterolemic effect of Chinese black tea extract in human subjects with borderline hypercholesterolemia
- Anti-hyperglycemic effect of black tea (Camellia sinensis) in rat
- The effect of an extract of green and black tea on glucose control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: double-blind randomized study
- Modulatory effects of black v. green tea aqueous extract on hyperglycaemia, hyperlipidaemia and liver dysfunction in diabetic and obese rat models
- Glucose-lowering effect of powder formulation of African black tea extract in KK-Ay/TaJcl diabetic mouse
- Effect of Kombucha, a fermented black tea in attenuating oxidative stress mediated tissue damage in alloxan induced diabetic rats
- Effects on blood pressure of drinking green and black tea
- The effect of consuming instant black tea on postprandial plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in healthy humans

Atractylodes Marcocephala Extract
- Effects of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidzumi rhizome on 3T3-L1 adipogenesis and an animal model of obesity
- β-Eudesmol (a main component of Atractylodes lancea)-induced potentiation of depolarizing neuromuscular blockade in diaphragm muscles of normal and diabetic
- Studies on physico-chemical properties and hypoglycemic activity of complex polysaccharide AMP-B from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz
- Stimulating effects on mouse splenocytes of glycoproteins from the herbal medicine Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.
- Antioxidant ability and mechanism of rhizoma Atractylodes macrocephala
- Sesquiterpenoids from Atractylodes macrocephala act as farnesoid X receptor and progesterone receptor modulators
- Effects of Radish Seed, Dandelion and Atractylodes Macrocephala on Muscles of Stomach and Duodenum in Rabbit [J]
- The roots of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidzumi enhanced glucose and lipid metabolism in C2C12 myotubes via mitochondrial regulation
- The metabolism of polysaccharide from Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz and its effect on intestinal microflora
- Ethanol extract of Atractylodes macrocephala protects bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast differentiation
- Anti-obesity effect of Pinellia ternata extract in Zucker rats
- Pinellia ternata Breitenbach attenuates ovalbumin-induced allergic airway inflammation and mucus secretion in a murine model of asthma
- Effects of Pinellia ternata (Thunb.) Berit. on the metabolomic profiles of placenta and amniotic fluid in pregnant rats
- Effect of oral administration of Pinellia ternata, Zingiberis rhizoma and their mixture on the efferent activity of the gastric branch of the vagus nerve in the rat
- Transgenic Tobacco Expressing Pinellia ternata Agglutinin Confers Enhanced Resistance to Aphids
- Quantitative analysis of anti-emetic principle in the tubers of Pinellia ternata by enzyme immunoassay
- An anti-emetic principle of Pinellia ternata tuber
- Studies on Stimulating Components of Raw Pinellia ternata (Thunb.)(Banxia)
- Effect of Pinellia ternata tuber on the efferent activity of the gastric vagus nerve in the rat
- Effect of Pinellia ternata lectin on membrane currents of mouse motor nerve terminals.
- Coptis chinensis alkaloids exert anti-adipogenic activity on 3T3-L1 adipocytes by downregulating C/EBP-α and PPAR-γ
- Anti-diabetic effect of Coptis Chinensis polysaccharide in high-fat diet with STZ-induced diabetic mice
- Anti-Diabetic Effects of a Coptis chinensis Containing New Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula in Type 2 Diabetic Rats
- Studies on the hypoglycemic effect of Coptis chinensis and berberine
- Hypoglycemic and Hypocholesterolemic Effects of Coptis chinensis Franch Inflorescence
- Antimicrobial properties of berberines alkaloids in Coptis chinensis Franch by microcalorimet
- Coptis chinensis Franch. exhibits neuroprotective properties against oxidative stress in human neuroblastoma cells
- Coptis chinensis inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth through nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene activation
- Antiinflammatory effects of a combined herbal preparation (RAH13) of Phellodendron amurense and Coptis chinensis in animal models of inflammation
- Neuroprotective Effect of Coptis chinensis in MPP and MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Models
- The Efficacy and Tolerability of Adjunctive Alternative Herbal Medicine (Salvia miltiorrhiza and Pueraria lobata) on Vascular Function and Structure in Coronary
- Effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza hydrophilic extract on antioxidant enzymes in diabetic patients with chronic heart disease: a randomized controlled trial
- Cardiovascular protective effects of adjunctive alternative medicine (Salvia miltiorrhiza and Pueraria lobata) in high-risk hypertension
- Extraction, preliminary structural characterization, and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge
- Ameliorating effects of compounds derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza root extract on microcirculatory disturbance and target organ injury by ischemia and reperfusion
- The protective effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza in an animal model of early experimentally induced diabetic nephropathy
- Constituents with α-glucosidase and advanced glycation end-product formation inhibitory activities from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge.
- Inhibition of interleukin-12 and interferon-γ production in immune cells by tanshinones from Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Aqueous extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza attenuates increased endothelial permeability induced by tumor necrosis factor-α
- Effects of purified herbal extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza on ischemic rat myocardium after acute myocardial infarction

- Antihypertensive Effects of Gynura procumbens Extract in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
- Hypoglycemic effect of combination of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. and Gynura procumbens (Lour.) Merr. ethanolic extracts standardized by rutin
- Rice Cakes Containing Dietary Fiber Supplemented with or without Artemisia Annua and Gynura Procumbens Merr. Alleviated the Risk Factors of Metabolic
- Effects of an ethanolic extract of Gynura procumbens on serum glucose, cholesterol and triglyceride levels in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Antidiabetic properties and mechanism of action of Gynura procumbens water extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Flavonoid identification and hypoglycaemic studies of the butanol fraction from Gynura procumbens
- Hypoglycemic and anti–hyperglycemic study of Gynura procumbens leaf extracts
- Antidiabetic effect of Gynura procumbens leaves extracts involve modulation of hepatic carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Hypoglycemic effects of Gynura procumbens fractions on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats involved phosphorylation of GSK3β (Ser-9) in liver
- The effect of extraction temperature on total phenols and antioxidant activity of Gynura procumbens leaf

Higenamine Nelumbo nucifera (lotus seeds)
- Antiobesity and hypolipidemic effects of lotus leaf hot water extract with taurine supplementation in rats fed a high fat diet
- Ethanol extract of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) root exhibits an anti-adipogenic effect in human pre-adipocytes and anti-obesity and anti-oxidant effects in rats fed a high
- Chemical constituents from Nelumbo nucifera leaves and their anti-obesity effects
- Higenamine 4′-O-β-D-glucoside in the lotus plumule induces glucose uptake of L6 cells through β2-adrenergic receptor
- Groups of Diabetic KK-CAy Mice Specifically Bred for High and Low Sensitivity to Exogenous Acetylcholine and β1-Adrenergic Stimulation: Interaction of Higenamine
- The relaxation effect and mechanism of action of higenamine in the rat corpus cavernosum
- Acute oral intake of a higenamine-based dietary supplement increases circulating free fatty acids and energy expenditure in human subjects
- Higenamine inhibits apoptosis and maintains survival of gastric smooth muscle cells in diabetic gastroparesis rat model via activating the β2-AR/PI3K/AKT pathway
- Higenamine reduces HMGB1 during hypoxia-induced brain injury by induction of heme oxygenase-1 through PI3K/Akt/Nrf-2 signal pathways
- Higenamine (Norcoclaurine) as stimulant and fat burner
Oleuropein
- Oleuropein attenuates visceral adiposity in high‐fat diet‐induced obese mice through the modulation of WNT10b‐ and galanin‐mediated signalings
- Effects of olive oil and its minor phenolic constituents on obesity-induced cardiac metabolic changes
- Evaluation of hypocholesterolemic effect of oleuropein in cholesterol-fed rats
- Oleuropein aglycone enhances UCP1 expression in brown adipose tissue in high-fat-diet-induced obese rats by activating β-adrenergic signaling
- Beneficial effects of the olive oil phenolic components oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol: focus on protection against cardiovascular and metabolic diseases
- Hypoglycemic and antioxidant effect of oleuropein in alloxan-diabetic rabbits
- Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Effects of Hydroxytyrosol and Oleuropein from Olive Leaves in Alloxan-Diabetic Rats
- Oleuropein offers cardioprotection in rats with simultaneous type 2 diabetes and renal hypertension
- Antihyperglycemic effect of thymoquinone and oleuropein, on streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus in experimental animals
- Hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic and antiatherogenic effects of oleuropein in alloxan-induced Type 1 diabetic rats
Warnings:
As with any supplement, consult your medical practitioner prior to using this product if you are pregnant, may become pregnant, breastfeeding, taking medication, other dietary supplements or have a medical condition.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
*Daily Value has not been established
Shipping Countries: Armenia
Ready to ship in 1-3 business days
Additional information
| Weight | 0.200 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 30 × 30 × 30 cm |
| Weight | 25g, 100g |



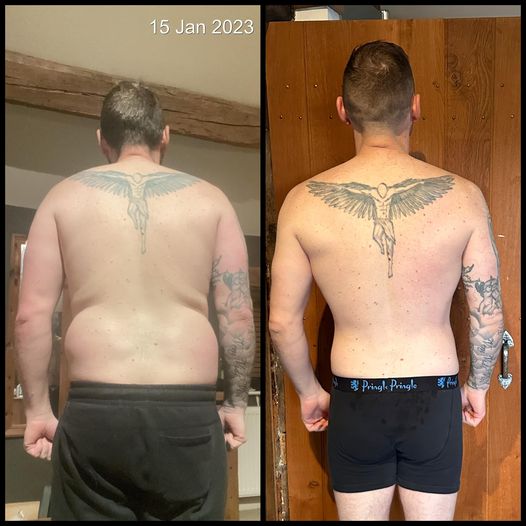































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.